What you’ll learn
- how GraphQL HTTP requests are handled by the deployed cloud infrastructure and application code
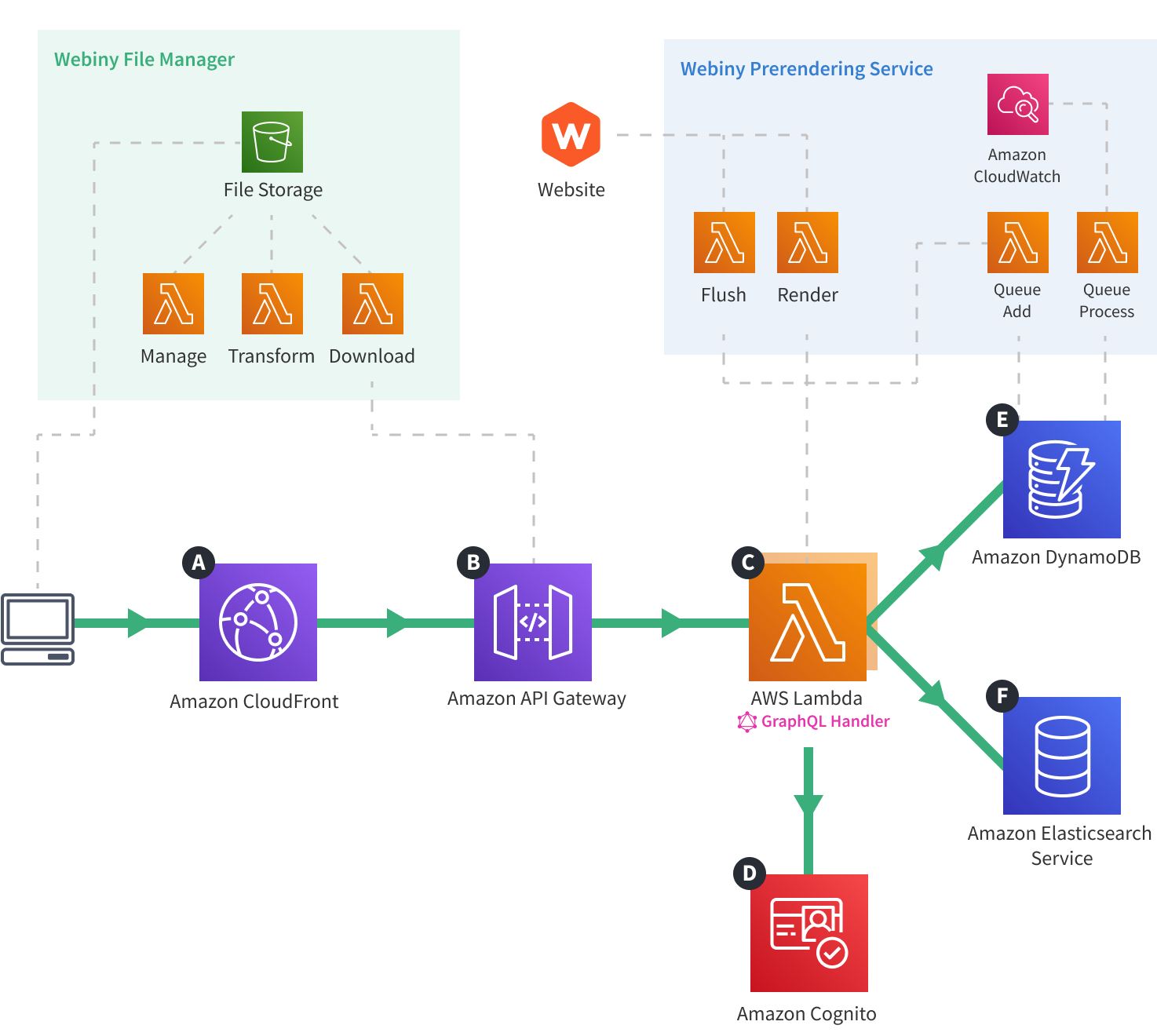
Diagram
What you’ll learn
For brevity, the diagram doesn’t include network-level cloud infrastructure resources, like region, VPC, availability zones, and so on. Check out the Default VPC and Custom VPC topics if you’re interested in that aspect of the deployed cloud infrastructure.
Description
The diagram shows how HTTP requests (GraphQL queries and mutations) travel through the deployed cloud infrastructure. Request are primarily issued by the Admin Area, or Website applications, but of course, can be issued by other clients as well.
The steps are the following:
- The GraphQL HTTP request first reaches the Amazon CloudFront
A . - The request is forwarded to the Amazon API Gateway
B . - The Amazon API Gateway invokes the GraphQL Server Lambda function
C . - Depending on the issued GraphQL operation, the Lambda function’s code may issue one or more requests to other cloud infrastructure resources:
- Amazon Cognito
D to perform identity authentication - Amazon DynamoDB
E or Amazon ElasticSearch ServiceF to perform database queries
- Amazon Cognito
- Once the code execution has completed, an HTTP response is returned back to the Amazon API Gateway
B . - The Amazon API Gateway
B forwards the request to the Amazon CloudFrontA , which again forwards it back to the client.